Describe the Gross Anatomy of the Female Breast
Describe the shape and position of the female breast. It is intended primarily for undergraduate and graduate medical school students and residents who are preparing for or reviewing the clinical anatomy of the breast.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/636/Mu51j1549B1jGkdOOCtAJA_the-lymphatics-of-the-female-breast_english.jpg)
Female Breast Anatomy Blood Supply And Mammary Glands Kenhub
Breast buds- small mound of breast and nipple develops.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/636/Mu51j1549B1jGkdOOCtAJA_the-lymphatics-of-the-female-breast_english.jpg)
. It lies superficially to the pectoralis major and serratus anterior muscles. Breast and areola enlarge. The mammary mam ă-r ē.
The remaining part is made up of fatty tissue. List the blood supply of the female breast. The breast is located on the anterior thoracic wall.
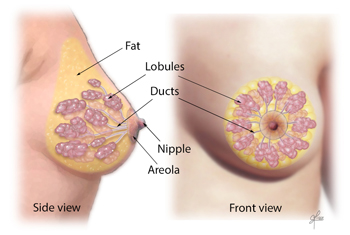
Each of these lobes is made up of many smaller lobules the gland that produces milk in nursing women. Relating to breasts glands are the organs of milk production and are located in the breasts fig-ure 1913. The human breast houses the mammary gland that produces and delivers milk through development of an extensive tree-like network of branched ducts.
Describe the structure of the mammary gland. Currently the lactating breast is described in Grays Anatomy Bannister et al. A healthy female breast is made up of 1220 sections called lobes.
The human breast consists of the parenchyma and stroma originating from ectodermal and mesodermal elements respectively. These breast structures are generally where the cancer begins to form. The breast of an adult woman is a milk- producing tear-shaped gland.
Both the lobes and lobules are connected by milk ducts which act as stems or tubes to carry the milk. They are arranged like the petals of a daisy. Anatomically the adult breast sits atop the pectoralis muscle the pec chest muscle which is atop the ribcage.
The mons pubis is a pad of fat that is located at the anterior over the pubic bone. The medical name for breast is mammary gland. Only small elevated nipple.
The breast tissue extends horizontally side-to-side from the edge of the sternum the firm flat bone in the middle of the chest out to the midaxillary line the center of the axilla or underarm. The nipple is surrounded by the areola with has small bumps areolar glands. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers.
Nipple is flush with breast surface. Describe the blood supply to the female reproductive tract. The resource may be used in the lecture hall as a primary or.
Visceral pleura forms the outermost layer of the lungs. Anatomy of the Breasts. The female breast- a mound of tissue overlying the pectoralis major and has 2 regions the body with the nipple at the apes the ancillary tail-an extension towards the armpit.
Each lobe has many smaller structures called lobules. The lobes lobules and bulbs are all linked by thin tubes called ducts. Describe the lymphatic drainage of the female breast.
These end in dozens of tiny bulbs that can produce milk. It is supported by and attached to the front of the chest wall on either side of the sternum by ligaments. The breasts are paired structures located on the ventral thorax.
Conical to pendulous body with the nipple and then extension toward the arm pit called the axillary tail. It extends horizontally from the lateral border of the sternum to the mid-axillary line. 15-20 secretory lobes.
Trace the female reproductive tract and describe the gross anatomy and histology of each organ. The breast can be considered to be composed of two regions. The female breast consists of 1020 lobes that are surrounded by connective and adipose tissue.
Each breast consists of tissue overlying the chest wall muscles the pectoral muscles. These ducts lead to the nipple in the center of a dark area of skin called the areola. Pleural cavity lies between the visceral and parietal pleura.
5 rows Key facts about the female breast. List the three layers of the uterus from superficial to. Upper medial quadrant 2.
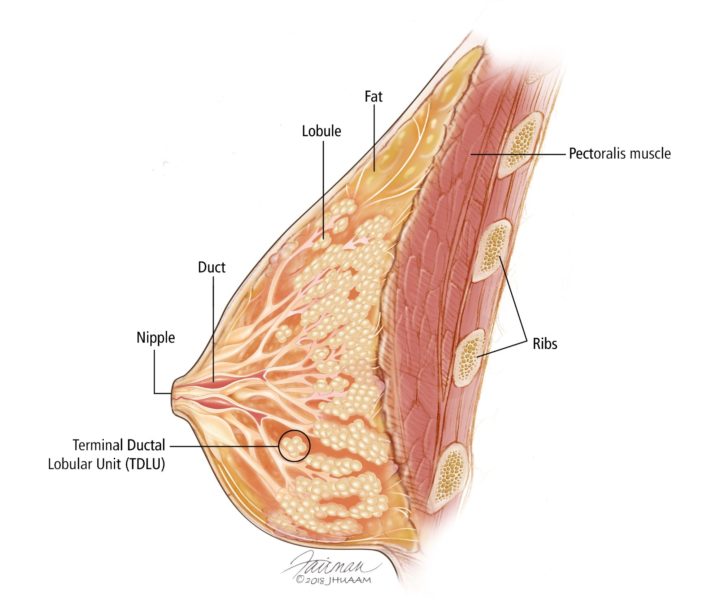
Anatomy of the breast. Each lobe contains milk-producing glandular structures and multiple terminal duct lobular units that form the milk duct system and drain via the major milk ducts and the. Upper lateral quadrant 3.
Describe the gross anatomy of the female breast. It contains a small film of. 1995 as being composed of glandular and adipose tissue held together by a loose framework of fibres called Coopers ligaments.
The lungs are enclosed by the double-layered pleural sac. The female breasts or mammary glands are the modified appendages lying on the anterior chest wallIt is present in males as well but in most men it is not as prominent as it is in females. Development of the human breast is distinctive for several reasons.
After puberty it becomes covered in pubic hair. Identify the ligaments that support the female reproductive organs. Positioned over the pectoral muscles of the chest wall and attached to the chest wall by fibrous strands called coopers.
The female breast has a role in both nourishing the offspring as well as offering immunological protection to the newborn babyTo some degree the breast also has a psychological function. Vertically it spans between the 2nd and 6th costal cartilages. Within each lobe are smaller structures called lobules where milk is.
Gross anatomy of the normal breast definition. List the three layers of the uterus from superficial to deep. This resource is a short image-intensive PowerPoint demonstration of the gross and pathologic anatomy of the breast.
List the components of the vulva. In women the breasts are composed principally of specialised tissue glandular tissue that produces milk. Describe the external anatomy of the male or female breast structures relation to pectoralis major Mound of tissue overlying the pectorals major.
Describe the applied anatomy in the. Each breast has 15 to 20 sections called lobes. The mammary glands are modified sweat glands.
Lower medial quadrant 4. The milk-producing part of the breast is organized into 15 to 20 sections called lobes. The areola and nipple form a secondary mound over the breast.
The major organs of the female reproductive system are located inside the pelvic cavity. Position extent 23 rests on pectoralis major 13 on serratus anterior while its lower medial edge just overlaps the upper part of the rectus sheath. Parietal pleura lines the pulmonary cavities.
The external female reproductive structures are referred to collectively as the vulva Figure 2. Identify and describe the gross anatomy of the mammary glands o Lactiferous Ducts - ducts that connect the mammary glands to the nipple and allow for the transport of milk o Nipple - projection in which mammary ducts terminate o Lobules - contains clusters of alveoli o Lactiferous sinus - area of milk collection between alveoli and lactiferous duct. Externally each of the breasts of both males and females has a raised nipple surrounded by a circular pigmented area called the areola ă-r ē ō-l ă.
OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture the student should be able to.
Breast Anatomy Breast Cancer Breastfeeding Conditions
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/overview_image/415/kiHQzH2QbHXVdXORyjIg_female-breast-structure_english.png)
Female Breast Anatomy Blood Supply And Mammary Glands Kenhub
Overview Of The Breast Breast Pathology Johns Hopkins Pathology
No comments for "Describe the Gross Anatomy of the Female Breast"
Post a Comment